Navigating Time: A Comprehensive Look at Solar and Lunar Calendars
Related Articles: Navigating Time: A Comprehensive Look at Solar and Lunar Calendars
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Time: A Comprehensive Look at Solar and Lunar Calendars. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Time: A Comprehensive Look at Solar and Lunar Calendars

Throughout history, humanity has sought to understand and track the passage of time. This need has led to the development of various calendar systems, with two fundamental types standing out: solar calendars and lunar calendars. Each system offers unique perspectives on timekeeping, reflecting different cultural and astronomical observations. Understanding these systems sheds light on the diverse ways civilizations have organized their lives and celebrated their traditions.
Solar Calendars: The Dance of the Sun
Solar calendars are primarily based on the Earth’s revolution around the sun. The year in a solar calendar is defined by the time it takes for the sun to appear to complete a full cycle through the zodiac, returning to its original position as observed from Earth. This cycle, known as the solar year, is approximately 365.2422 days long.
Solar calendars strive to align with the seasons, ensuring that the solstices and equinoxes fall on consistent dates within the calendar year. This alignment is crucial for agricultural societies, as it allows for the prediction of planting and harvesting seasons, ensuring food security.
Key Features of Solar Calendars:
- Focus on the Sun: The year is defined by the Earth’s orbit around the sun.
- Seasonal Alignment: Calendar months are synchronized with the solstices and equinoxes, reflecting the changing seasons.
- Accuracy in Tracking Seasons: Solar calendars offer a more accurate representation of the Earth’s annual journey around the sun.
- Widely Adopted: Solar calendars are the dominant calendar system in the modern world, used by most nations for official purposes.
Notable Examples of Solar Calendars:
- Gregorian Calendar: The most widely used calendar in the world, adopted by many countries for official purposes. It’s a solar calendar with adjustments to account for the Earth’s elliptical orbit, ensuring a precise alignment with the seasons.
- Julian Calendar: The predecessor to the Gregorian calendar, established by Julius Caesar. While largely accurate, it faced challenges in accurately representing the Earth’s orbit, leading to the adoption of the Gregorian calendar.
- Persian Calendar: A solar calendar used in Iran and some other countries. It features a leap year system based on a 33-year cycle, ensuring accurate alignment with the seasons.
Lunar Calendars: The Rhythms of the Moon
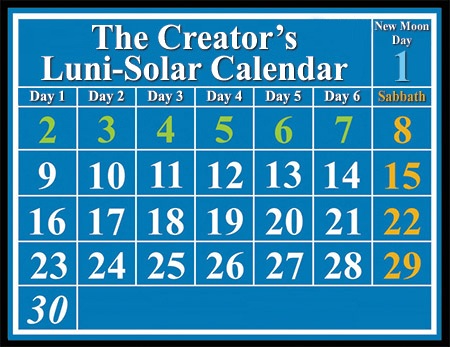
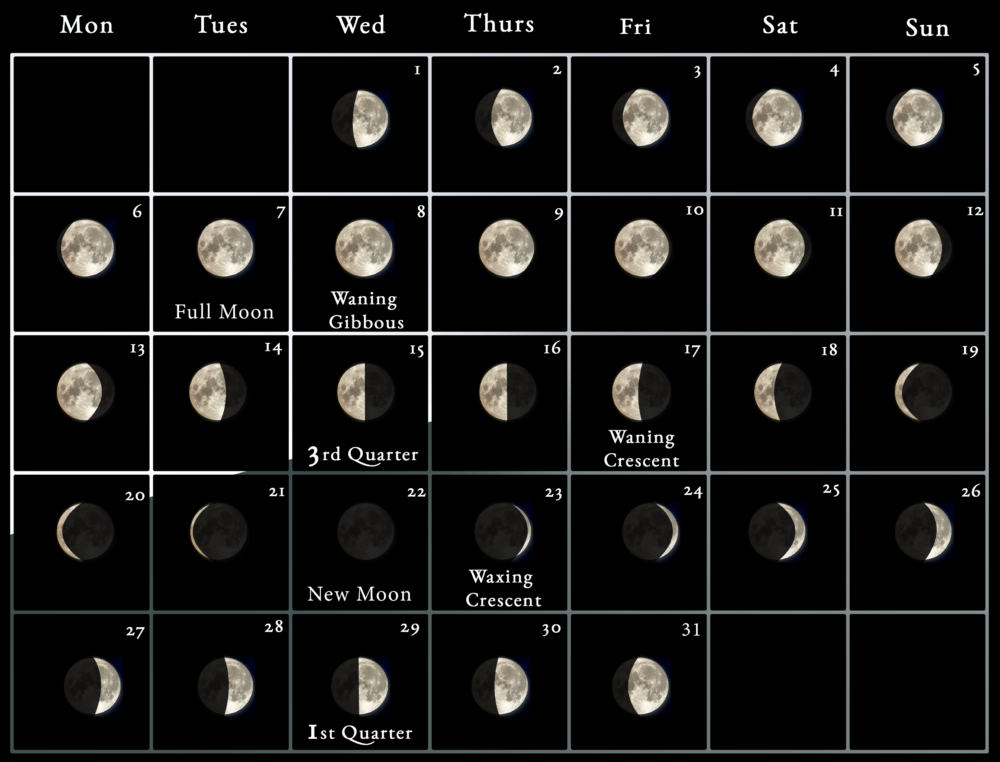
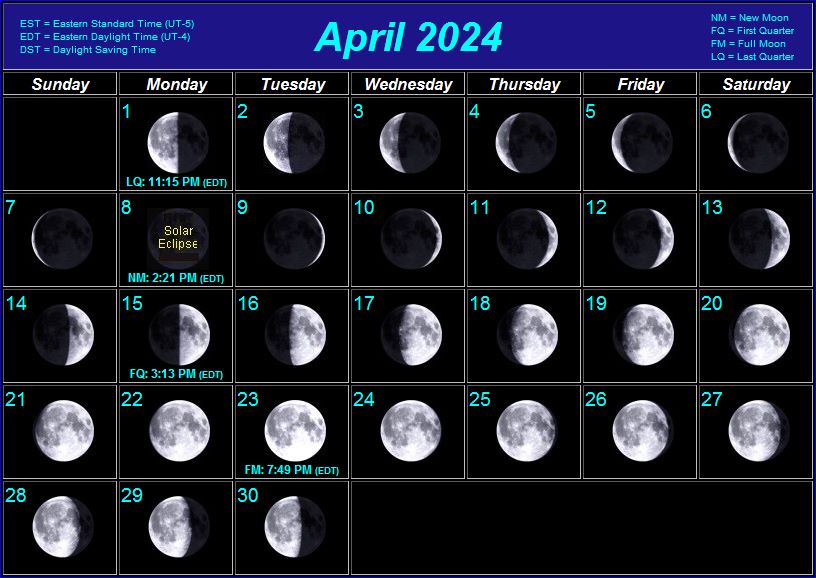
Lunar calendars are based on the cycles of the moon. The month in a lunar calendar is defined by the time it takes for the moon to complete a full cycle of phases, from new moon to full moon and back again. This cycle, known as the synodic month, is approximately 29.5 days long.
Lunar calendars are often associated with religious and cultural practices, as the moon’s phases have held spiritual and symbolic significance in many societies. They are also used for tracking menstrual cycles and for predicting tides.
Key Features of Lunar Calendars:
- Focus on the Moon: The month is defined by the lunar cycle, with each month beginning with a new moon.
- Short Months: Lunar months are shorter than solar months, typically lasting 29 or 30 days.
- Regular Adjustments: Lunar calendars often require adjustments to align with the solar year, as the lunar cycle is shorter than the solar year.
- Cultural and Religious Significance: Lunar calendars are often deeply embedded in cultural and religious traditions.
Notable Examples of Lunar Calendars:
- Islamic Calendar: A purely lunar calendar used by Muslims worldwide. It is based on the observation of the moon’s phases, with months beginning with the sighting of the new moon.
- Hebrew Calendar: A lunisolar calendar used by Jewish communities. It combines lunar months with a leap year system to ensure alignment with the solar year.
- Chinese Calendar: A lunisolar calendar used in China and some other East Asian countries. It incorporates both lunar and solar elements, with months based on the lunar cycle and a leap month added every two or three years to synchronize with the solar year.
The Interplay of Solar and Lunar Calendars: Lunisolar Calendars
Many cultures have developed lunisolar calendars, which combine elements of both solar and lunar calendars. These calendars use lunar months but include adjustments to ensure alignment with the solar year. This approach allows for the tracking of both lunar cycles and seasonal changes.
Key Features of Lunisolar Calendars:
- Combination of Lunar and Solar Elements: Months are based on lunar cycles, while adjustments are made to synchronize with the solar year.
- Leap Months: Leap months are added periodically to ensure alignment with the solar year.
- Diverse Applications: Lunisolar calendars are often used for religious and cultural purposes, as well as for tracking agricultural cycles.
Notable Examples of Lunisolar Calendars:
- Hebrew Calendar: As mentioned earlier, the Hebrew calendar is a lunisolar calendar, incorporating a leap year system to align with the solar year.
- Chinese Calendar: The Chinese calendar is a complex lunisolar calendar with a rich history, combining lunar months with a leap month system.
The Importance of Understanding Solar and Lunar Calendars
Understanding the differences between solar and lunar calendars provides valuable insights into the diverse ways civilizations have navigated time. These systems are not merely abstract concepts but reflect the profound influence of celestial bodies on human cultures and societies.
Benefits of Studying Solar and Lunar Calendars:
- Cultural Understanding: Exploring different calendar systems offers a deeper understanding of diverse cultures and their unique perspectives on time.
- Historical Insights: Calendar systems provide valuable clues about the development of civilizations, their agricultural practices, and their religious beliefs.
- Scientific Appreciation: Studying calendars enhances our appreciation for the complex interplay between the Earth, the sun, and the moon, fostering a deeper understanding of astronomy.
- Contemporary Relevance: Understanding different calendar systems is increasingly relevant in a globalized world, promoting greater cultural awareness and appreciation for diverse perspectives.
FAQs: Solar and Lunar Calendars
Q: What is the main difference between a solar calendar and a lunar calendar?
A: A solar calendar is based on the Earth’s revolution around the sun, while a lunar calendar is based on the moon’s cycles.
Q: Why do some calendars have leap years?
A: Leap years are introduced in some calendars to account for the fact that the solar year is not a whole number of days. Leap years help maintain alignment with the seasons.
Q: How do lunisolar calendars work?
A: Lunisolar calendars combine elements of both solar and lunar calendars. They use lunar months but include adjustments to align with the solar year.
Q: Are solar calendars more accurate than lunar calendars?
A: Solar calendars are more accurate in tracking the seasons, as they are based on the Earth’s orbit around the sun. However, lunar calendars are useful for tracking the moon’s phases and for religious and cultural purposes.
Q: Which calendar system is best?
A: There is no "best" calendar system. The most appropriate calendar system depends on the specific needs and priorities of a particular culture or society.
Tips for Understanding Solar and Lunar Calendars:
- Visualize the Earth’s Movement: Imagine the Earth orbiting the sun and the moon orbiting the Earth to better understand the principles behind solar and lunar calendars.
- Explore Different Cultures: Learn about the calendar systems used by different cultures around the world to gain a broader perspective on timekeeping.
- Track the Moon’s Phases: Observe the moon’s phases over a month to appreciate the lunar cycle and its influence on calendar systems.
- Connect Calendars to Seasons: Notice how the seasons change throughout the year and how solar calendars are designed to align with these changes.
Conclusion
Solar and lunar calendars offer distinct perspectives on timekeeping, reflecting the influence of celestial bodies on human societies. Understanding these systems enriches our appreciation for the diverse ways civilizations have organized their lives, celebrated their traditions, and navigated the passage of time. From the ancient Egyptians to the modern world, these calendar systems continue to shape our understanding of the universe and our place within it. By exploring the intricacies of solar and lunar calendars, we gain a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of humanity, nature, and the cosmos.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Time: A Comprehensive Look at Solar and Lunar Calendars. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!