Unveiling the Power of Calendar Spreads: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Options Trading
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Calendar Spreads: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Options Trading
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Calendar Spreads: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Options Trading. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Calendar Spreads: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Options Trading

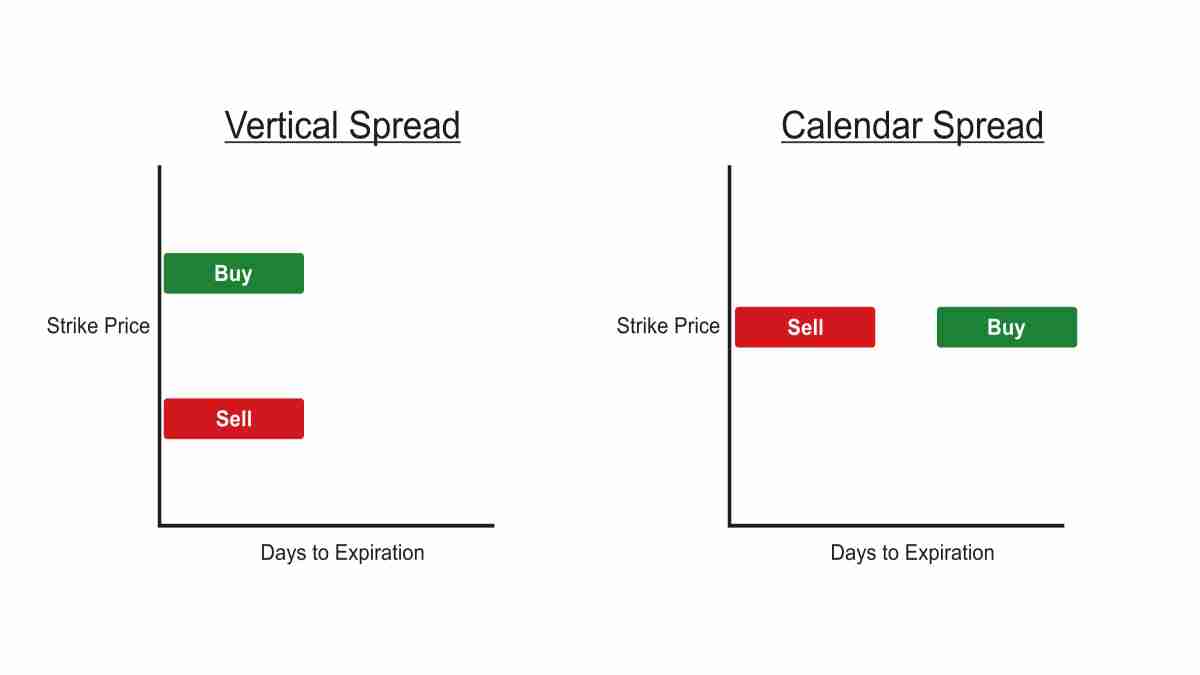
In the dynamic world of options trading, calendar spreads emerge as a powerful strategy for experienced traders seeking to profit from time decay and volatility. This strategy, often referred to as a "time spread," involves simultaneously buying and selling options contracts with different expiration dates but the same underlying asset and strike price. This article delves into the intricacies of calendar spreads, exploring their mechanics, advantages, disadvantages, and practical applications.
Understanding the Fundamentals
A calendar spread is constructed by purchasing a longer-dated option (the "long leg") while simultaneously selling a shorter-dated option (the "short leg"). The key to this strategy lies in the interplay between time decay and volatility. The longer-dated option is expected to have a higher premium due to its extended time value, while the shorter-dated option will have a lower premium due to its shorter time value. The difference in premiums represents the initial profit or loss of the spread.
Types of Calendar Spreads
Calendar spreads can be classified into two main types, depending on the trader’s market outlook:
-
Bullish Calendar Spread: This spread is constructed when the trader anticipates an increase in the underlying asset’s price. It involves buying a longer-dated call option and selling a shorter-dated call option. The trader profits from the difference in premiums as the underlying asset price rises and the longer-dated option gains more time value.
-
Bearish Calendar Spread: This spread is constructed when the trader anticipates a decrease in the underlying asset’s price. It involves buying a longer-dated put option and selling a shorter-dated put option. The trader profits from the difference in premiums as the underlying asset price falls and the longer-dated option gains more time value.
The Mechanics of Profit and Loss
The profit and loss profile of a calendar spread is determined by the underlying asset’s price movement and the time remaining until expiration.
-
Profit Potential: The maximum profit potential of a calendar spread is limited to the initial difference in premiums. This occurs when the underlying asset price remains relatively stable or experiences a moderate move in the expected direction.
-
Loss Potential: The maximum loss potential of a calendar spread is unlimited, although the likelihood of a large loss decreases as the underlying asset price moves in the expected direction.
Advantages of Calendar Spreads
-
Limited Risk: Calendar spreads offer limited risk compared to other options strategies, as the maximum loss is capped at the initial premium difference. This makes them attractive to risk-averse traders.
-
Time Decay Advantage: The strategy benefits from the passage of time, as the shorter-dated option loses time value faster than the longer-dated option. This can contribute to profit generation, particularly when the underlying asset price remains relatively stable.
-
Volatility Management: Calendar spreads can be used to manage volatility, as the short leg provides a hedge against adverse price movements.
-
Flexibility: Calendar spreads offer flexibility, as they can be constructed with various expiration dates and strike prices, allowing traders to tailor the strategy to their specific market outlook and risk tolerance.
Disadvantages of Calendar Spreads
-
Limited Profit Potential: The maximum profit potential is limited to the initial premium difference, which may be relatively small.
-
Unfavorable Price Movements: If the underlying asset price moves significantly against the trader’s expectation, the loss potential can be substantial.
-
Time Decay Risk: While time decay can be an advantage, it also poses a risk if the underlying asset price does not move in the expected direction within the shorter-dated option’s timeframe.
Practical Applications of Calendar Spreads
-
Earnings Announcements: Calendar spreads can be used to profit from the volatility associated with earnings announcements. By selling a shorter-dated option expiring before the announcement and buying a longer-dated option expiring after the announcement, traders can benefit from the potential price swings.
-
Market Uncertainty: Calendar spreads can be implemented in periods of market uncertainty, as they provide a way to profit from time decay while limiting risk.
-
Volatility Reduction: Calendar spreads can be used to reduce portfolio volatility by hedging against adverse price movements.
FAQs about Calendar Spreads
Q1: How do I calculate the profit/loss of a calendar spread?
A1: The profit/loss of a calendar spread is calculated as the difference between the premium received for selling the shorter-dated option and the premium paid for buying the longer-dated option. This difference represents the initial profit or loss, which can be adjusted by the underlying asset price movement.
Q2: What are the risks associated with calendar spreads?
A2: The primary risks associated with calendar spreads include:
-
Unlimited Loss Potential: While the maximum loss is capped at the initial premium difference, the underlying asset price can move significantly against the trader’s expectation, resulting in substantial losses.
-
Time Decay Risk: The shorter-dated option loses time value faster, which can be detrimental if the underlying asset price does not move in the expected direction within its timeframe.
-
Volatility Risk: If the underlying asset’s volatility increases significantly, it can lead to larger losses.
Q3: How do I choose the appropriate expiration dates for a calendar spread?
A3: The choice of expiration dates depends on the trader’s market outlook and risk tolerance. For example, a trader expecting a significant price movement might choose a wider time gap between the expiration dates, while a trader anticipating a moderate price movement might choose a narrower time gap.
Q4: What are the advantages of using a calendar spread over other options strategies?
A4: Calendar spreads offer advantages over other options strategies, such as:
-
Limited Risk: The maximum loss is capped at the initial premium difference, making them attractive to risk-averse traders.
-
Time Decay Advantage: The strategy benefits from the passage of time, as the shorter-dated option loses time value faster.
-
Volatility Management: Calendar spreads can be used to manage volatility, as the short leg provides a hedge against adverse price movements.
Tips for Implementing Calendar Spreads
-
Define Your Market Outlook: Clearly identify your expectation for the underlying asset’s price movement.
-
Choose Appropriate Expiration Dates: Select expiration dates that align with your trading timeframe and market outlook.
-
Manage Risk: Implement appropriate risk management techniques, such as setting stop-loss orders.
-
Monitor the Spread: Continuously monitor the spread’s performance and adjust your position as needed.
-
Consider the Underlying Asset: Analyze the underlying asset’s historical volatility and price trends to inform your strategy.
Conclusion
Calendar spreads offer a compelling options trading strategy for experienced traders seeking to profit from time decay and volatility. By understanding the mechanics, advantages, and disadvantages of this strategy, traders can effectively implement calendar spreads to achieve their desired trading outcomes. The limited risk, potential for profit generation, and flexibility of calendar spreads make them a valuable tool in a diversified options trading portfolio. However, it is crucial to remember that this strategy is not without risks, and traders should carefully consider their market outlook and risk tolerance before implementing calendar spreads.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Calendar Spreads: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Options Trading. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!